The ERTMS/ETCS has its own language to transmit information (to balises, radios, ...). The latter is based on variables, packets, messages, and telegrams [1]. For this article, we will focus on variables. What are they? In which form do they have to be (rules)? And which organizations are responsible for their assignment?
Definition of variables
Variables are what are used by ERTMS/ETCS to encode single data values. Variables cannot be split in minor units. The whole variable has one type. To create them, there are some rules that should be taken into consideration. The rules are described in the next part.
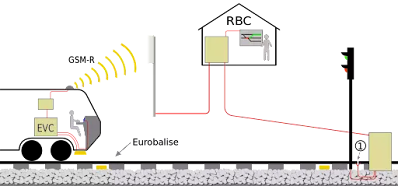 |
| Illustration of the functioning of ETCS Level 2 Photo Credit: François Melchior |
Rules
Prefixes
When it comes to variables, there is always at the beginning of each one, one of these prefixes according to the function/description:
- Acceleration (A_)
- Distance (D_)
- Gradient (G_)
- Length (L_)
- Miscellaneous (M_)
- Number (N_)
- Class Number (NC_)
- Identity Number (NID_)
- Qualifier (Q_)
- Time/Date (T_)
- Speed (V_)
- Text (X _)
Other rules
In addition to the prefixes, as mentioned above, there are other rules such as[2]:
- Variables may have special values which are related to the basic meaning of the variable
- Special values have always the highest values in a variable
- Spare values are located between the normal and special values in the variable range
- Names of variables are unique. A variable is used in context with the meaning as described in the variable definition. Variables with different meanings have different names.
- When transmitting over the different transmission media, the most significant bit shall be transmitted first.
- Boolean variables always use 0 for false and 1 for true.
- All variable definitions are independent of the transport media over which they are used, if used in more than one media.
Responsible organizations
- ERA: for variables that need international coordination,
- Member States: for variables that need national coordination
- Date of submission.
- Information about the submitter.
- Information about the request.
Link: https://www.era.europa.eu/sites/default/files/activities/docs/ertms_etcs_variables_form_en.doc

0 Comments
Post a Comment